About
"Emotate is the world's first emotional social network."
Have you ever felt strongly emotional that you wanted to share it with your friends online? Of course you have, we are social and emotional beings after all. How would you phrase it? Maybe you would add a youtube link of a song that describes how you feel? You would probably add an emoticon from many emoticons that vary from site to site.
How would people who see your post respond to it? Would they "fav" it or "like" it? What does a "like" really mean? Would they just comment on it, trying to explain to you how they feel towards what they've just read or seen? If a post is sad and somebody likes it, what did that person want to tell you?
And lastly, can you imagine digital messaging without text smileys? When somebody responds to your message with "Ok.", do you feel anxious? Do you have trouble getting these messages into context? How does that person feel about you?
Emotions and thoughts never go one without other. That's why Emotate was built with a strong focus on emotional communication and expression. It tries to solve the problem of the lack of emotional expression in the existing communication mediums, by providing a unique way for you to:
- emotionally express yourself,
- be emotionally understood,
- gain emotional feedback.
The name emotate is a made up word combining two words: "emotion" and "annotate". It allows you to do exactly that, to form a detailed emotional notation and pair it with written text. Although it contains all of the features of a social network it was envisioned to be used more as a blog or journal than a classic social network. This way of usage was intended so it's users will be more focused on expressing themselves rather then being engaged in constant communication.
It is very easy to mix emotions with feelings. You can feel hungry, and that is a feeling. But you can also feel sad, and you are feeling an emotion. A feeling corresponds to having sense of your inner or outer changes or states of your organism and/or environment which are often connected to basic existentional needs, like being sleepy, being hungry, tired, hot, energetic, in pain, etc... But notice that when you think about sensing the emotion "sadness", you actualy feel sad because of some feeling ivoked in you and/or from some external situation. You can say that you are sad because you feel hunger and you realize that there is nothing to eat. By realizing your inner state of hunger indicated by high levels of hormone Ghrelin that creates the feeling of hunger, and external enviromental state of having no food you set yourself in a learned conscious mode (mood, might that be sadness or fear in low intensity creating only a feeling of discomfort). Emotions act as universal language to express to others that you are in distress and to receive needed help by emphaty that you invoke in them. Or to paraphrase the book "Emotions" by Robert Plutchik, each of the basic emotions are corespondant to 8 basic existentional prototypes of behaviour.
To conclude, you can feel an emotion, so emotion is a feeling or set of feelings, but not all feelings are an emotion. Feelings are more concrete (instinctive) and emotions are more abstract (conscious). Emotion is a state manifesting itself in a inner, hormonal, and external, behavioural, way caused by subjective conscious interpretation of an inner or outer state. To better understand it, here is one more example: "I am so angry because people disrespect me, my head is boilning." Being angry here is an abstract term to describe your inner state created by hormonal changes triggered by realizing the idea of being disrespected. You just dont get born with the idea of disrespect, that is a conscious and learned conclusion in a very early stage of developement. Being disrespected moreover casted away is a basic existentional fear. So as a pattern of fighting for survival hormone of stress cortisol and maybe hormone of fear adrenaline are excreted causing increased blood floow into the head thus making you feel hot headed. As you can see a border between emotions and feelings is rather thin and emotions are definitely a complex topic that needs more research and emphasis which is one of the main goals of this project.
Idea to improve online emotional expression by providing a novel standardized emotional notation and moreover a novel user interface to accompany it, we decided to research the topic of emotions as much as we could. After finding different theories and explanations, we chose one that for us represented a solid start upon which we will base our system, and that is Robert Plutchik's Theory of Emotions. This theory was especialy sutable because it provided us with a unique method of emotional cateogrization with two types, separating emotions on basic and complex and explaining the value of emotional intensity thus enabling us to fit more emotional terms into a smaller space of the user interface. Robert Plutchik's theory had more to offer. It's ingenious diagram of basic emotions, their intensities and basic neighbourhood combined complex emotions, called "Wheel of Emotions" (Illustration 1), gave us also an initial idea for the main part of our user interface, "Emotate Wheel" (Illustration 2). But in order to test and expand this theory we decided to make changes and improve the number of emotion terms that will be available to users. With a help of English Dictionary and Thesaurus we were able to find more terms semantically suitable for the solution and make some changes. There was also a feeling that presented emotional terms are not enough so we decided to provide users of this system with the ability to submit their own opinions on complex emotions and contribute by suggesting new combinations they discovered empirically.
Basic emotions
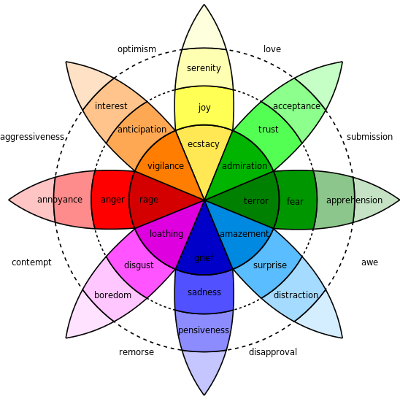
Theory that we've set as a base presents 8 basic emotions: joy, acceptance, fear, surprise, sadness, disgust, anger, anticipation, with three levels of intensity. Each of these basic emotions corresponds to 8 basic behavioral prototypes as noted before. Plutchik's ingenious diagram (Illustration 1) is constructed so it shows the correlation of neighboring basic emotions and provides insight into their possible levels of intensity. The big problem of emotion terms is their different meaning especially by intesity from culture to culture, so the originally provided number was probably small due to that reason and for the purpose of easier setting the fundation of the theory. By having that in mind and the desire to expand the given set and provide users with more options we decided to introduce two more levels of intensitiy giving the sum of 5 levels, as it can be seen on Table 1, where 1 is the weakest, 5 is the strongest and 3 is the middle often having the name of the emotion family itself.
As said before emoticons emerged with digital messaging to fulfill the purpose of giving them emotional dimension. We noticed that the ones standardized by usage are correspondant to 8 basic emotions: joy :D, acceptance :), fear :C , surprise :o, sadness :(, disgust :P, anger >:\ and anticipation :S. So we decided that they should have a special place in our system to tell the reader, on the first look, how the author of the emotional notation feels. Minimalistic representative emoticon images, presented in Table 1 and applied in Illustration 2, were created for that purpose.
Also each basic emotion has it's own colour and each intensity a different shade that fades alongside the intensity respectively, as depicted in the original diagram. Colors are especially important for visual distinction, and paired with emoticons can give a fast insight, without reading, on the author's feelings. All aspects of the Plutchik's theory were gathered through scientific methods and are backed with statistics, including the colors.
Complex emotions
Other emotions are complex and they constist of feeling more than one basic emotion at a time. It might be very hard to separate basic emotions that are contained in a complex one just because we have adopted it under their unique terms as an unique inner state. But we go with a presumption that just like you can feel more than one feeling at a time, you can feel more than one emotion. You can say I'm angry that there is no food and I am sad that there is noone that takes care of my needs (Example taken from studying my girlfriend's emotional behaviour). In that case you might feel offended that someone's actions created your current stuation. Depending of the intensity of basic emotions, the complex emotion of being offended might have a different feel to it, ether a person is more angry or more sad.
Basic pairs
Basic emotions in the diagram are arranged with a reason. Pairing each basic emotion with it's neighboring one gives resulting complex emotion. Plutchik's theory shows only one intensity of these complex emotions, but we were sure they can have intensity dimension too. We collected synonims for each of the results of basic pairs and ordered them by intesity. Average number of synonims to the original terms was two, so we decided upon three levels of intensity, where the most intensive was the original term. Level of intensity of these complex emotions depends on the intensitiy of it's parents. Final set of basic emotions, their five intensity levels and the three intensity levels of combined neighboring emotions is presented bellow in Table 1.
|
int |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
1 |
interest |
optimism |
serenity |
sympathy |
tolerance |
obedience |
concern |
fright |
distraction |
|
2 |
curiosity |
content |
approval |
apprehension |
uncertainty |
||||
|
3 |
anticipation |
enthusiasm |
joy |
fondness |
acceptance |
submission |
fear |
shock |
surprise |
|
4 |
attentiveness |
euphoria |
elation |
love |
trust |
awe |
panic |
horror |
amazement |
|
5 |
vigilance |
ecstasy |
respect |
terror |
astonishment |
|
int |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
1 |
distraction |
disagreement |
pensiveness |
pity |
boredom |
spite |
annoyance |
irritation |
interest |
|
2 |
uncertainty |
gloominess |
dislike |
hostility |
curiosity |
||||
|
3 |
surprise |
fail |
sadness |
remorse |
aversion |
contempt |
anger |
aggressiveness |
anticipation |
|
4 |
amazement |
disappoint-ment |
sorrow |
misery |
disgust |
hate |
rage |
destructive-ness |
attentiveness |
|
5 |
astonishment |
grief |
loathing |
fury |
vigilance |
Conflicting pairs
Presented order of emotions in the diagram depicts one more feature. Each emotion combined with it's opposite one results in confusion or inner conflict. It doesn't mean that someone can't feel acceptance and disgust in the same time, it means that feeling these two emotions creates a state of inner confusion.
- acceptance + disgust = conflict
- anger + fear = conflict
- anticipation + surprise = conflict
- joy + sadness = conflict
Distant pairs
Combinations presented below might be slightly modified from original theory. Only one of the them has three intensity levels which are condtioned by intensity levels of it's parents.
- acceptance + anger = dominance
- acceptance + anticipation = fatalism
- acceptance + sadness = depression
- anticipation + disgust = cynicism
- anticipation + fear = insecurity | worry | anxiety *Depending on the intensity of basic emotions
- anticipation + sadness = pessimism
- anger + joy = pride
- anger + sadness = offended
- anger + surprise = outrage
- disgust + fear = shame
- disgust + joy = morbidness
- disgust + surprise = repulsion
- fear + sadness = guilt
- fear + joy = thrill
- joy + surprise = delight
Special cases
- respect (acceptance with intensity 5) + joy = admiration
Triplets
- anger + anticipation + sadness = jealousy
- anger + disgust + joy = schadenfreude
- disgust + fear + surprise = embarrassment
- acceptance + fear + sadness = humiliation
- anger + sadness + surprise = frustration
- acceptance + anticipation + joy = lust
Presented modified set of emotions contains 88 different emotion terms, sorted in 8 basic emotions with 5 levels of inthensity for each, 3 levels of intensity for 8 complex emotions from combined neighboring emotions, 17 from pairs of basic emotions, 6 fom combining three basic emtions, 1 special pair case and 1 term describing conflicting pairs.